Adding Meshing to Your Project
By placing the standard ARMeshManager in a scene, developers can access a live mesh that allows virtual objects to interact with the real-world environment.
For example, a virtual ball thrown into a meshed scene will realistically bounce off of the floor and walls.
When the Niantic Spatial SDK (NSDK) is enabled in Unity, meshing is still provided through Unity's AR Foundation Meshing Subsystem and enabled with the standard ARMeshManager.
NSDK overrides the default implementation and provides Niantic Spatial's proprietary meshing technology through the standard interface.
Niantic Spatial Meshing works on lidar and non-lidar devices running either Android or iOS.
For support on lidar devices, ensure that the Prefer LiDAR if Available setting is checked in Niantic Lightship SDK Settings and an AROcclusionManager is present in your scene.
Mesh Chunks
To lighten the application's compute workload as the mesh grows, NSDK breaks the mesh up into chunks.
The three-dimensional world is divided into a regular grid of "blocks" of a fixed size.
When meshing is running, new mesh chunks will be created in the scene Hierarchy underneath XROrigin > Trackables.
Each block has its own renderer and collider defined by the Mesh Prefab specified in the ARMeshManager.
Mesh chunks are continually updated as new data is added to the 3D representation.
Meshing Extensions
To offer more configurability than the standard ARMeshManager, NSDK provides an optional Lightship Meshing Extension component.
Lightship Meshing Extension provides extra options to allow you to tweak meshing rules for distance, quality and clean-up.
Add a Lightship Meshing Extension component to the same game object as ARMeshManager to gain access to these settings:
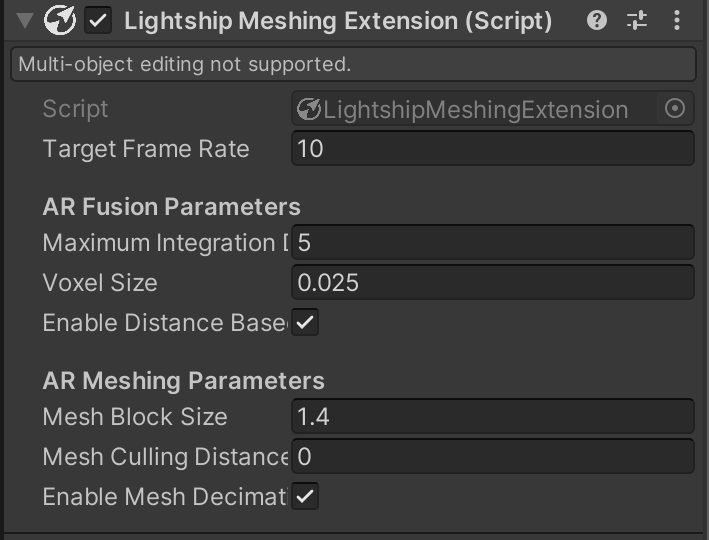
- Target Frame Rate: The number of times per second to run the mesh update routine. This should be no higher than the AR Session update rate.
- Fuse Keyframes Only: Enabling this improves mesh accuracy at the cost of a lower update frequency.
- AR Fusion Parameters:
- Maximum Integration Distance: The far distance threshold from the device sensor for integrating depth samples into the 3D scene, in meters. New mesh blocks will not be generated further than this distance from the camera.
- Voxel Size: The size of individual voxel elements in the scene, in meters. Higher values will save memory but also reduce the precision of the surfaces.
- Enable Distance-Based Volumetric Cleanup: Enable this to save memory and smooth latency by cleaning up already-processed elements in the feature's volumetric representation (once they move outside the region where new meshes are generated). This will not remove previously-generated mesh.
- AR Meshing Parameters:
- Mesh Block Size: The size of the mesh blocks used for generating the mesh filter and mesh collider.
- Mesh Culling Distance: The distance from the user where mesh blocks will be removed from the scene. Set to 0 to disable distance-based culling.
- Enable Mesh Decimation: Enable to save memory by removing excess triangles from the mesh.
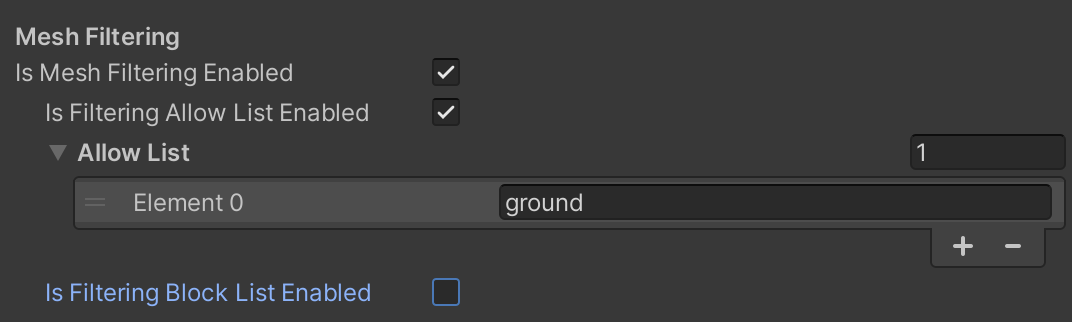
- Mesh Filtering:
- Is Mesh Filtering Enabled: Check this box to enable mesh filtering. See Mesh Filtering for more information.
- Semantic Segmentation Manager: When mesh filtering is enabled, an
AR Semantic Segmentation Managercomponent is required in the scene. - Allow List: If populated, only these semantic classes will be allowed in the mesh.
- Block List: If populated, these semantic classes will be excluded from the mesh.
- Experimental Meshing Options:
- Enable Levels of Detail: Check this box to enable the experimental level of detail meshing feature which saves memory and reduces latency. For more information, see the Meshing Level of Detail feature page.
Mesh Filtering
Mesh Filtering uses semantic segmentation to identify sections of a mesh as common parts of the world, such as ground or sky, then uses that information to determine what should be part of the final mesh with a user-defined allowlist and blocklist.
For example, a blocklist containing sky would remove the sky from the final mesh, while an allowlist containing ground would exclude everything but the ground.
See How to Exclude Semantic Channels with Mesh Filtering for more information.

Long-Distance Meshing
These settings are only recommended for high-end devices. For information on supported devices, see the Google ARCore device list and Apple ARKit device list.
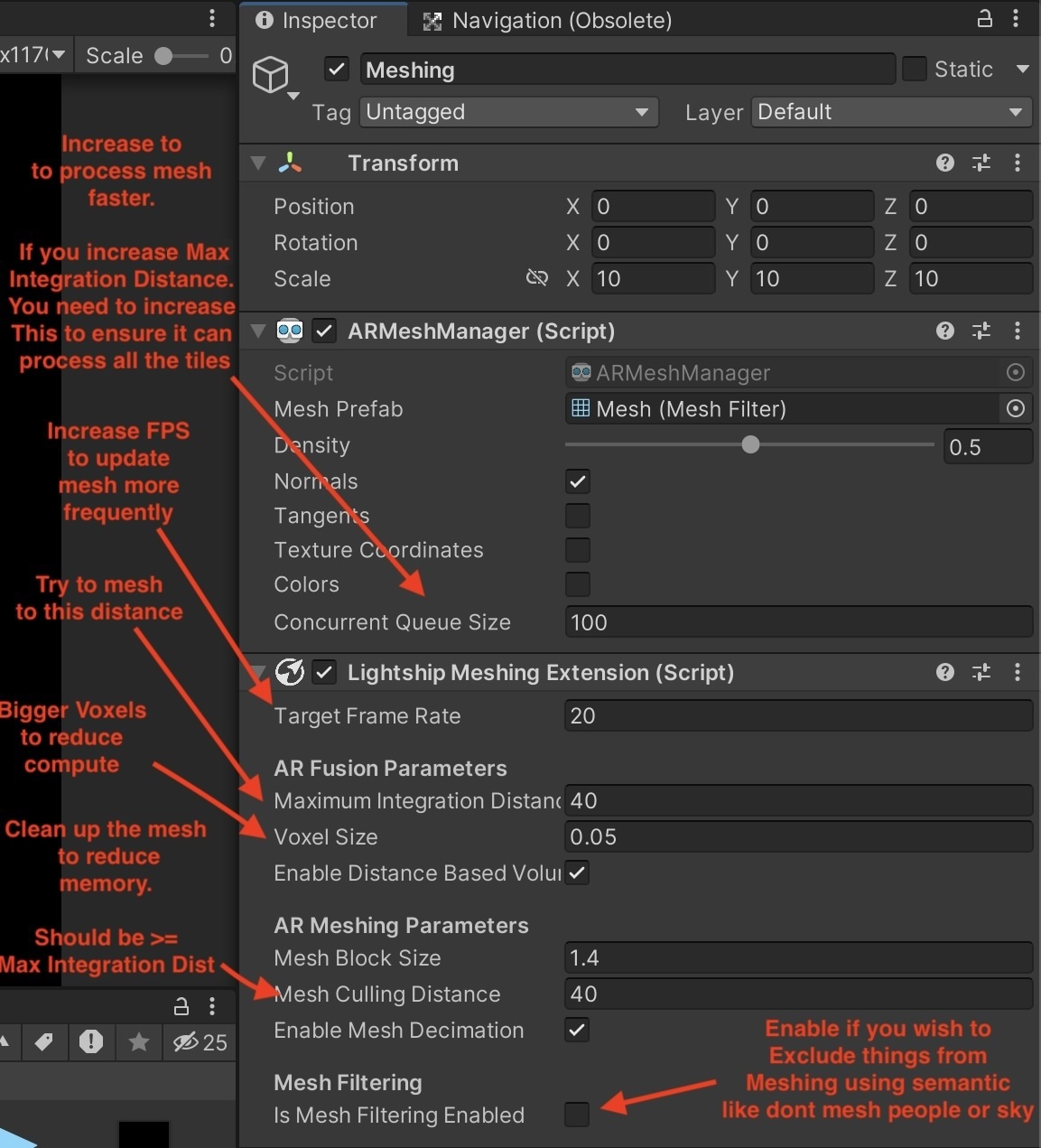
You can configure your application to mesh over much longer distances by increasing the Voxel Size, turning on Enable Distance-Based Volumetric Cleanup and increasing the Maximum Integration Distance and Mesh Culling Distance to between 20 and 40 meters. For example, try out the following settings:
- Target Frame Rate: 20
- AR Fusion Parameters:
- Maximum Integration Distance: 40
- Voxel Size: 0.05
- Enable Distance-Based Volumetric Cleanup: True
- AR Meshing Parameters:
- Mesh Block Size: 1.4
- Mesh Culling Distance: 40 (should be >= Maximum integration distance)
- Enable Mesh Decimation: True
If you use these settings, increase the Concurrent Queue Size setting in the ARMeshManager component as well to make sure that the manager can keep up with the amount of tiles being surfaced.
This will increase CPU and GPU usage, so we recommend testing thoroughly on a variety of devices.

Lidar Devices
On lidar devices, it is possible to use Niantic Spatial Meshing with either lidar depth or NSDK depth. To use lidar depth, ensure that Prefer LiDAR if Available is enabled in the Niantic Lightship SDK settings menu (Lightship top menu > Settings) and that an AROcclusionManager is present in the scene. (Note that meshing will still be supported even if No Occlusion is selected as the Occlusion Preference Mode.)
Lidar depth will only support a maximum integration distance of around five meters. If you wish to generate mesh blocks farther away from the user, disable Prefer LiDAR if Available to use NSDK depth instead.
More Information
The NSDK sample project includes an example of running meshing.
See How to Exclude Semantic Channels with Mesh Filtering for a guide of how to set up a project with meshing.
See How to Add Physics to a Meshed Scene for how to use meshing to simulate realistic collisions.
See How to Add Navigation Mesh for how to use meshing to create navigation paths for agents.